
When a positive and a negative ion form a chemical bond, its an ionic. The purpose of cathodic protection (CP) systems is to prevent corrosion in metals. In chemistry, an ionic bond is a connection between two ions with opposite charges.
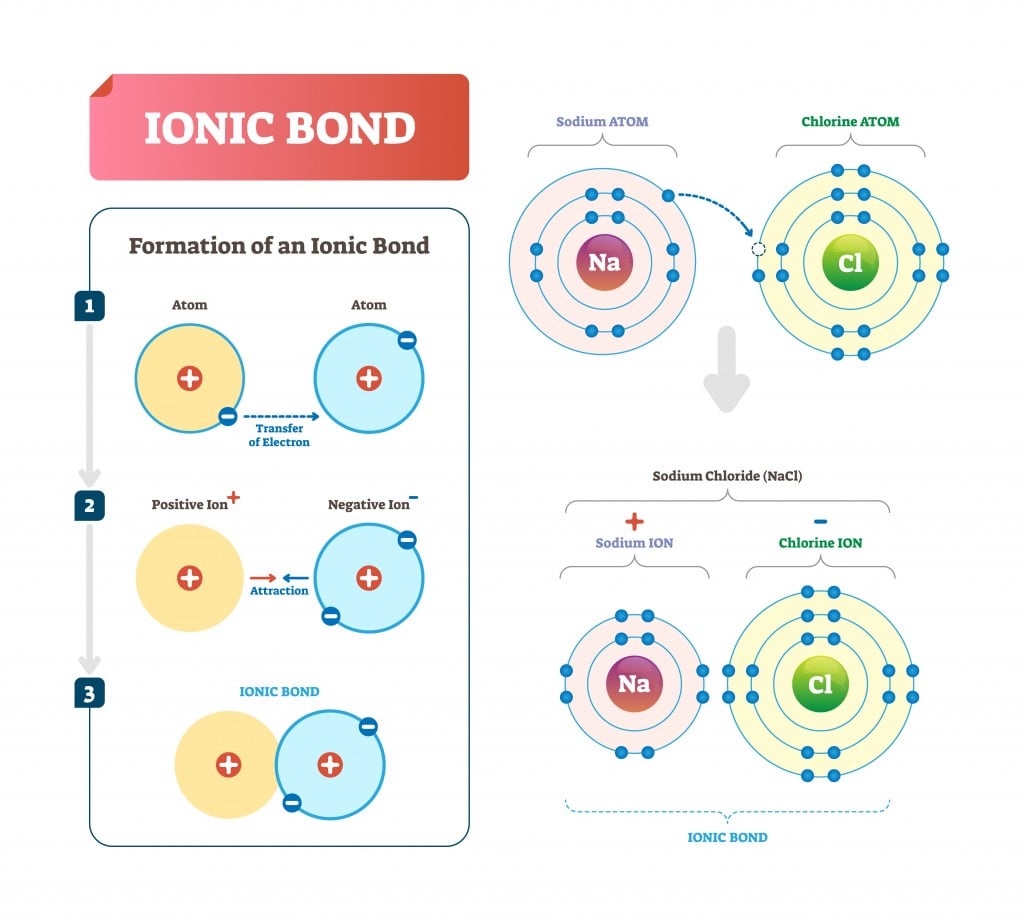
It is a loss of adhesion between a cathodic coating and its metal substrate due to a cathodic reduction reaction (corrosion reaction) taking place. An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through an electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. If there are no defects in the coating, then cathodic disbondment does not occur.Ĭathodic disbondment protection shows a much more consistent performance when the coating thickness is over 200 microns therefore, coating thicknesses less than 200 microns should be avoided to achieve good cathodic disbondment protection. Disbonding is the failure of a coating to adhere to the substrate to which it was applied. This results in a voltage drop at the interface and causes cathodic disbondment. The bond forms when the atom with less than 4 valence electrons (Sodium) gives its electrons to the atom. As the size of the fault or defect increases, the current forces more coating away from the metal. There are four types of bonds or interactions: ionic, covalent, hydrogen bonds, and van der Waals interactions. Ionic bonds connect a metal and nonmetal element.

Figure 1: Models for part of the giant sodium. The electrostatic attraction between newly formed cations. The amount of current flow through a defect or fault depends on the size of the coating fault. An ionic bond is an electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions of a chemical compound. Ionic bonding occurs when electrons transfer between atoms, with a concurrent formation of ions. Here the current passes through any faults, cracks or defects in the metal coating. Bonding Definition: A guarantee of performance required, either by law or consumer demand, for many businesses, most typically general contractors, temporary personnel agencies, janitorial. When the electrons being shared are so unevenly distributed between the atoms the bond that is formed is called an ionic bond.

In cathodic protection (CP) systems, the coating disbonding from a metal surface may occur because an electric current passes through the metal surface that needs to be protected, which frees up the hydrogen atoms that cause the coating disbondment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
